-Arrays are defined in much the same manner as ordinary variables, except that each array name must be accompanied by a size specification (i.e., the number of elements).
-An array is a collection of variables of the same type that are referred to through a common name. A specific element in an array is accessed by an index.
-An array is a group of related data items that share a common name.
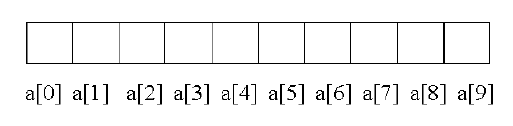
-The individual values are called elements. The elements are: a[0], a[1], a[2] .......a[9].
-The name of the array(a) contains the address of the first location i.e., a[0].
-The elements are stored in continuous memory locations during compilation.
-The elements of the array are physically and logically adjacent. When an array is passed as an argument to a function, its address is actually passed.
-The lowest address corresponds to the first element and the highest address to the last element.
-For a one-dimensional array, the size is specified by a positive integer expression(size), enclosed in square brackets. The expression is usually written as a positive integer constant.
-In general terms, a one-dimensional array definition may be expressed as
storage_class data_type array[ expression] ;
-The storage-class is optional, default values are automatic(auto) for arrays that are defined within a function or a block, and external( extern)for arrays that are defined outside of a function.
Eg: Several typical one-dimensional array definitions are shown below.
int x[100];
char text[80];
static char message[25];
static float n[12];
Integer arrays
int a[10];
/*defines an array a of size 10, as a block of 10 contiguous elements in memory */
Character Arrays
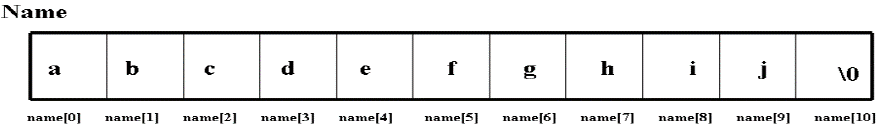
char name[11];
-To define a character array, need to define an array of size n+1 characters. This is because all character arrays are terminated by a NULL character (“\0”).
-Where name[0] through name[9] will contain the characters comprising the name, and name[10] will store the NULL character.
Types of Arrays
Basically, arrays can divide into two types. They are:
1. One Dimensional Array:
- An array with only one subscript is called a one-dimensional array or 1- d array. It is used to store a list of values, all of which share a common name and are separable by subscript values.
2. Two Dimensional Array:
- An array with two subscripts is termed a two-dimensional array.
- A two-dimensional array, it has a list of given variable-name using two subscripts. We know that a one-dimensional array can store a row of elements, so, a two-dimensional array enables us to store multiple rows of elements.
One-dimensional Arrays:
-The general form of declaring a one-dimensional array is
data_type array_name [size];
-Where data-type refers to any data type supported by C, array-name should be a valid C identifier, the size indicates the maximum number of storage locations (elements) that can be stored.
The general form of initializing an array of one-dimension is as follows:
data_type array_name [size] = {list of values};
-The values in the list are separated by commas.
-One array is used to store a group of values. A loop (using, for loop) is used to access each value in the group.
Two-dimensional array:
-An array with two subscripts is termed a two-dimensional array.
Eg: int a[] [];
-A two-dimensional array, it has a list of given variable -name using two subscripts. We know that a one-dimensional array can store a row of elements, so, a two-dimensional array enables us to store multiple rows of elements.
Eg: A table of elements or a Matrix representation.
-The syntax of declaring a two-dimensional array is:
data_type array_name [rowsize] [ colsize];
-Row size and column size should be integer constants.
-Total number of location allocated = (row size * column size).
-Row-number range from 0 to rowsize-1 and column-number range from 0 to colsize-1.
Eg: int m[3] [3];
Applications of Arrays:
1. Arrays are used to store a list of values.
2. Arrays are used to Perform Matrix Operations ( Addition, Multiplication & Transpose)
3. Arrays are used to implement Search Algorithms. ( Linear Search & Binary Search).
4. Arrays are used to implement Sorting Algorithms ( Insertion Sort, Bubble Sort, Selection Sort, Quick Sort, Merge Sort, etc.,).
5. Arrays are used to implement Data structures ( Stacks & Queues).
6. Arrays are also used to implement CPU Scheduling Algorithms.
Recommended Questions
Useful Files
Users Joined





-Arrays are defined in much the same manner as ordinary variables, except that each array name must be accompanied by a size specification (i.e., the number of elements).
-An array is a collection of variables of the same type that are referred to through a common name. A specific element in an array is accessed by an index.
-An array is a group of related data items that share a common name.
-The individual values are called elements. The elements are: a[0], a[1], a[2] .......a[9].
-The name of the array(a) contains the address of the first location i.e., a[0].
-The elements are stored in continuous memory locations during compilation.
-The elements of the array are physically and logically adjacent. When an array is passed as an argument to a function, its address is actually passed.
-The lowest address corresponds to the first element and the highest address to the last element.
-For a one-dimensional array, the size is specified by a positive integer expression(size), enclosed in square brackets. The expression is usually written as a positive integer constant.
-In general terms, a one-dimensional array definition may be expressed as
storage_class data_type array[ expression] ;
-The storage-class is optional, default values are automatic(auto) for arrays that are defined within a function or a block, and external( extern)for arrays that are defined outside of a function.
Eg: Several typical one-dimensional array definitions are shown below.
int x[100];
char text[80];
static char message[25];
static float n[12];
Integer arrays
int a[10];
/*defines an array a of size 10, as a block of 10 contiguous elements in memory */

Character Arrays
char name[11];
-To define a character array, need to define an array of size n+1 characters. This is because all character arrays are terminated by a NULL character (“\0”).
-Where name[0] through name[9] will contain the characters comprising the name, and name[10] will store the NULL character.

Types of Arrays
Basically, arrays can divide into two types. They are:
1. One Dimensional Array:
- An array with only one subscript is called a one-dimensional array or 1- d array. It is used to store a list of values, all of which share a common name and are separable by subscript values.
2. Two Dimensional Array:
- An array with two subscripts is termed a two-dimensional array.
- A two-dimensional array, it has a list of given variable-name using two subscripts. We know that a one-dimensional array can store a row of elements, so, a two-dimensional array enables us to store multiple rows of elements.
One-dimensional Arrays:
-The general form of declaring a one-dimensional array is
data_type array_name [size];
-Where data-type refers to any data type supported by C, array-name should be a valid C identifier, the size indicates the maximum number of storage locations (elements) that can be stored.
The general form of initializing an array of one-dimension is as follows:
data_type array_name [size] = {list of values};
-The values in the list are separated by commas.
-One array is used to store a group of values. A loop (using, for loop) is used to access each value in the group.
Two-dimensional array:
-An array with two subscripts is termed a two-dimensional array.
Eg: int a[] [];
-A two-dimensional array, it has a list of given variable -name using two subscripts. We know that a one-dimensional array can store a row of elements, so, a two-dimensional array enables us to store multiple rows of elements.
Eg: A table of elements or a Matrix representation.
-The syntax of declaring a two-dimensional array is:
data_type array_name [rowsize] [ colsize];
-Row size and column size should be integer constants.
-Total number of location allocated = (row size * column size).
-Row-number range from 0 to rowsize-1 and column-number range from 0 to colsize-1.
Eg: int m[3] [3];
Applications of Arrays:
1. Arrays are used to store a list of values.
2. Arrays are used to Perform Matrix Operations ( Addition, Multiplication & Transpose)
3. Arrays are used to implement Search Algorithms. ( Linear Search & Binary Search).
4. Arrays are used to implement Sorting Algorithms ( Insertion Sort, Bubble Sort, Selection Sort, Quick Sort, Merge Sort, etc.,).
5. Arrays are used to implement Data structures ( Stacks & Queues).
6. Arrays are also used to implement CPU Scheduling Algorithms.