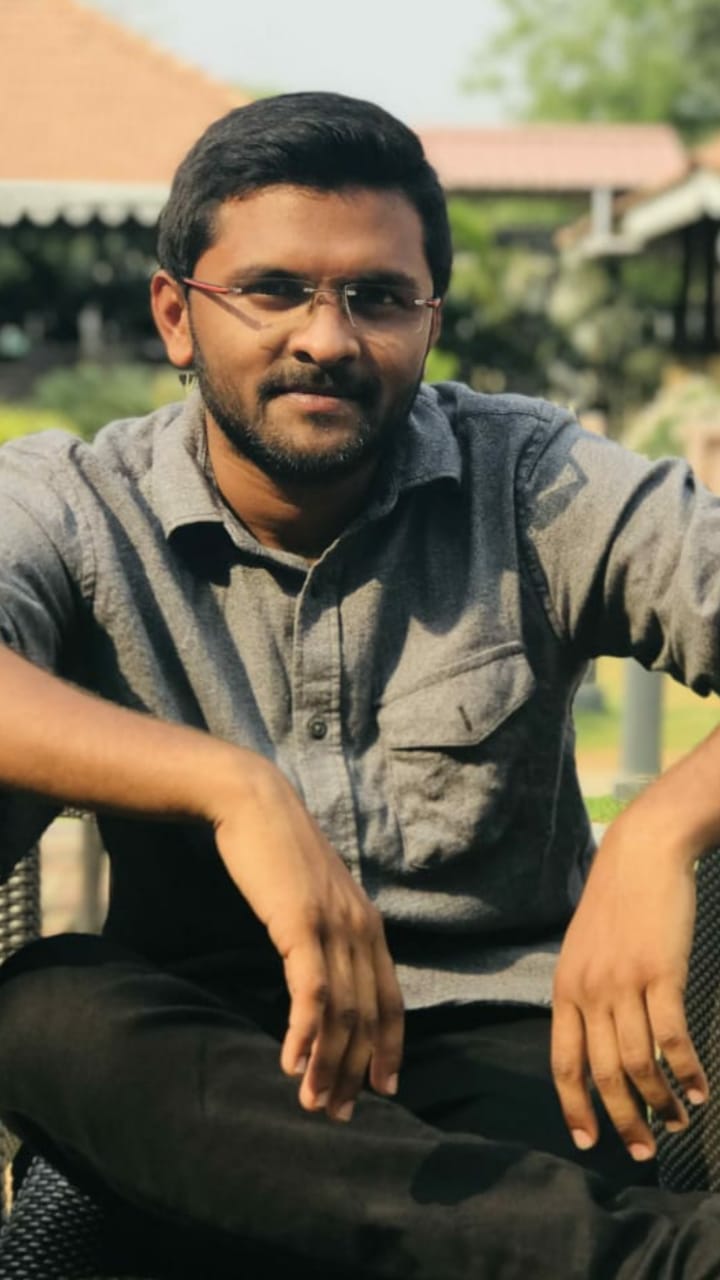
One can examine and observe the internal structure of a material at various levels of observation.The degree of magnification required to study a material by various methods is called a measure of the levels of observation.
Depending on the level, we can classify the structure of materials as:
1. Macro structure
2. Micro structure
3. Sub structure
4. Crystal structure
5. Electronic structure
6. Nuclear structure
1. Macro structure:
Macrostructure of a material is examined by low- power magnification or with naked eye. It deals with the shape, size and atomic arrangement in a crystalline material. The internal symmetry of the atoms in a crystalline material may reflect in the external form of a crystal such as quartz.
Macrostructure may be observed directly on a fracture surface or on a forging specimen. Macrostructure can reveal flaws,segregation; cracks etc., by using proper techniques. Large individual crystals of a crystalline material may be visible to the naked eye.
2. Micro structure:
This generally refers to the structure of the material observed under the optical microscope. Optical microscopes can magnify structures about 1500 to 3000 times linear, without loss of resolution of details of the material structure. The optical microscope can resolve two lines separately when their difference of separation is about 0.1 %u03BCm (10-7 m). Cracks, porosity, non-metallic insulations within materials can be revealed by examining them under powerful optical microscope.
3. Sub structure:
When crystal imperfections such as dislocation in a structure are to be examined, a special microscope having higher magnification and resolution than the optical microscope is used.Electron microscope with magnification 10 powerof 5 is used for this purpose.Another important modern
microscope is field ion microscope, which can produce images of individual atoms as well as defects in individual atomic arrangement.
4. Crystal structure:
It tells us the details of the atomic arrangement within a crystal. It is usually sufficient to study the arrangement of atoms within a unit cell. The crystal is formed by a very large number of unit cells forming regularly repeating patterns in space. The main technique employed for determining the
crystal structure is the X- ray diffraction and electron diffraction method. (Assemblies of atoms,geometries determined by bonding).
5. Electronic structure:
This usually refers to the electrons in the outermost shells of individual atoms that constitute the solid. Spectroscopic techniques are commonly used for determining the electronic structure.
6. Nuclear structure:
It is studied by nuclear spectroscopic techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mossbauer studies.
Recommended Questions
Useful Files
Users Joined





One can examine and observe the internal structure of a material at various levels of observation.The degree of magnification required to study a material by various methods is called a measure of the levels of observation.
Depending on the level, we can classify the structure of materials as:
1. Macro structure
2. Micro structure
3. Sub structure
4. Crystal structure
5. Electronic structure
6. Nuclear structure
1. Macro structure:
Macrostructure of a material is examined by low- power magnification or with naked eye. It deals with the shape, size and atomic arrangement in a crystalline material. The internal symmetry of the atoms in a crystalline material may reflect in the external form of a crystal such as quartz.
Macrostructure may be observed directly on a fracture surface or on a forging specimen. Macrostructure can reveal flaws,segregation; cracks etc., by using proper techniques. Large individual crystals of a crystalline material may be visible to the naked eye.
2. Micro structure:
This generally refers to the structure of the material observed under the optical microscope. Optical microscopes can magnify structures about 1500 to 3000 times linear, without loss of resolution of details of the material structure. The optical microscope can resolve two lines separately when their difference of separation is about 0.1 %u03BCm (10-7 m). Cracks, porosity, non-metallic insulations within materials can be revealed by examining them under powerful optical microscope.
3. Sub structure:
When crystal imperfections such as dislocation in a structure are to be examined, a special microscope having higher magnification and resolution than the optical microscope is used.Electron microscope with magnification 10 powerof 5 is used for this purpose.Another important modern
microscope is field ion microscope, which can produce images of individual atoms as well as defects in individual atomic arrangement.
4. Crystal structure:
It tells us the details of the atomic arrangement within a crystal. It is usually sufficient to study the arrangement of atoms within a unit cell. The crystal is formed by a very large number of unit cells forming regularly repeating patterns in space. The main technique employed for determining the
crystal structure is the X- ray diffraction and electron diffraction method. (Assemblies of atoms,geometries determined by bonding).
5. Electronic structure:
This usually refers to the electrons in the outermost shells of individual atoms that constitute the solid. Spectroscopic techniques are commonly used for determining the electronic structure.
6. Nuclear structure:
It is studied by nuclear spectroscopic techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mossbauer studies.